Sugarcane

Growth in sugar production in Cambodia has created significant potential for sugarcane-based biofuel production. That potential has not yet been realized, though recent foreign investment may give rise to change. There are several types of sugar crop: sugarcane, sugar palm trees and sugar beets. Sugarcane ...
Air pollution

The smoke and stench blow into the air in Phnom Penh’s huge landfill. Photo by Alan Morgan, taken on 17 September 2011. Licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0Air pollution originates mainly from the burning of fuels such as petroleum, diesel and coal in the transport, household, ...
Electricity infrastructure

Rural energy cooperative in Cambodia. Photo by Nomade Moderne, taken on 23 March 2006. Licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0The electricity distributed in Cambodia is partly generated within the country and partly imported. For many years, local generation was on a relatively small scale, and was ...
Energy for transport

In Cambodia, petroleum is traditionally the main source of energy for transportation. The petroleum fuels used for transportation include gasoline, diesel, heavy fuel and fuel oil. ...
Marine and coastal areas

In terms of attractiveness, one of Cambodia’s assets is the relative absence of intense development along its coasts, in comparison with neighboring countries. The 440 kilometer-long coastline includes a large area of non-urbanized zones, where locals can make their livelihoods from coastal resources. Cambodia’s coastline ...
Maternal and child health
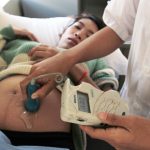
The number of mothers who died in labour has nearly halved over four years, from 182 fatalities in 2011 to 100 in 2015.175 Deaths among children have also dropped, although they remain comparatively high, and the prevalence of underweight newborns is high compared to many ...
Judiciary and courts

The judiciary is one of the three powers, together with the executive (the Government) and legislative (the National Assembly and the Senate), that constitute the state. 201 Its role is to monitor the application of the law and punish its violation. This power is vested ...
Forest protection support

Cambodia is struggling to safeguard its forests while preserving economic growth since many people make a living via farming, logging, and other activities that might lead to deforestation. Almost 80% of Cambodians living in rural regions rely on forests for survival. On the other hand, ...
Science and technology policy and administration

Cambodia has the ambition to transform and digitalize the government system and its economy. The overarching determination comes after the country’s ambitious economic goal of 2050, the readiness to keep up with the region’s science and technology development, and the global megatrend, the fourth industrial ...
Tourism

The Royal Government of Cambodia has acknowledged the potential of the tourism industry as a source of Cambodia’s socio-economy growth, including job creation and poverty reduction. Tourism has been considered one of Cambodia’s key economic pillars, both international and domestic. In the early 2000s, the ...
Sustainable Development Goals

In September 2015, the UN General Assembly adopted the new 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. This contained 17 items that have become known as the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), intended to drive action in critically important areas to the year 2030. These goals have ...
Education policy and administration

The Royal Government of Cambodia has continued its effort to reform the education sector at all levels. Over the years, policies and regulations have been enforced to improve education quality, accessibility, efficiency, effectiveness, inclusiveness, and transparency. Those policies and regulations include Education Strategic Plan 2019-2023, ...
Economic policy and administration

After the first general election in 1993, the government prepared and implemented a comprehensive micro- and macroeconomic policy and structural reform program to integrate Cambodia’s economy into the region and the world as well as stimulate its economic growth.545 In the two decades following that ...
SDG 15 Life on land

SDG 15 focuses on the sustainable use of terrestrial (land-based) biodiversity and ecosystems such as forests, grasslands, deserts and mountains and their interaction with freshwater systems. It aims to protect and restore their ecological function. The work includes applying sustainable land and forest management practices and ...




