International relations

Cambodia has strong diplomatic links with many countries. Its warmest relationship with a superpower is with the People's Republic of China. The most important economic ties are with China, the United states of America, Thailand and Vietnam. Cambodia is a member of the UN, AsEAN, ss='cambodia-color'>...
Aid and development

Following the Paris Peace Accords signed in October 1991, Cambodia has received a significant amount of global support for its development and post-conflict work. In 2014, 30 – 40 percent of the country’s national budget is funded through development assistance, placing Cambodia among the most ss='cambodia-color'>...
Asian Development Bank (ADB)

The Asian Development Bank (ADB) was established in 1966 which headquarter is in Manila and currently has 68 members under its institution. The ADB aims to assist members and partners by providing loans, technical assistance, grants, and investments to promote socio-economic development.1 The ADB has ss='cambodia-color'>...
Japanese aid

Japanese military members observe as Cambodian sailors attach a neck brace to a patient during a Pacific Partnership knowledge exchange in sihanoukville, Cambodia. Photo by U.s. Pacific Fleet, taken on 21 June 2014. Licensed under CC BY-NC 2.0Japan, through its official development branch called Japan ss='cambodia-color'>...
Community fisheries

Community fishery refuges, Battambang, Cambodia. Photo by Alan Brooks/WorldFish, taken on 2 November 2011. Licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.Fishing practices in Cambodia are classified into three broad categories: small-scale or family fishing, medium-scale and large-scale or commercial fishing.In 2001, aware of the need to safeguard ss='cambodia-color'>...
Social development

A trained medical staff listens to the heartbeat of an infant at 16 Makara hospital in Preah Vihear, Cambodia. Photo by The World Bank, taken on 30 January 2013. Licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.social development addresses profound social problems,81 especially poverty, unemployment and social exclusion, ss='cambodia-color'>...
Multilateral development assistance

Mr Il Oeur, director of Analysing Development Issues Centre (ADIC), a domestic NGO and WorldFish partner in Cambodia, leads a local dialogue session. Photo by WorldFish, taken on 27 June 2013. Licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0Multilateral aid is funding that is funneled between more than ss='cambodia-color'>...
Primary and secondary education

Article 68 of Cambodia’s Constitution states that the Government shall provide free primary and secondary education for all citizens and each individual shall pursue basic education for at least 9 years. Education is a fundamental engine of social and economic development for a country, especially ss='cambodia-color'>...
SDG 14 Life below water

SuStainable Development Goal 14 iS primarily about the interactionS of humanS with the oceanS. Specifically, it aimS to conServe and manage the uSe of oceanS, SeaS and marine reSourceS for SuStainable development.230 A UN General ASSembly call for action haS been uSed to clearly articulate SS='cambodia-color'>...
Plants

Although there are often new discoveries,302 a global lack of up to date data on botanical research makes plants biodiversity hard to assess in Cambodia. Compared to neighboring countries, the number of plant species is low, mostly due to the relative country’s flat landscape.303 Botanical knowledge ss='cambodia-color'>...
Fishing, fisheries and aquaculture

Cambodian fish farmer checking on fish quality. Photo by U.s. Agency for International Development (UsAID), taken on 16 October 2012. Licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.Cambodia’s inland capture fisheries are among the largest in the world. The fishing industry encompasses subsistence, commercial and recreational fishing, as ss='cambodia-color'>...
Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports

H.E. Hang Chuon Naron and Julie Chung in the inauguration of the Rice Academy, Cambodia. Photo by U.S EmbaSSy Phnom Penh, take on 17 September 2014. LicenSed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0In 1996, the MiniStry of Education, Youth and Sport&nbSp;(MoEYS) waS eStabliShed.351 ItS organization and functioning SS='cambodia-color'>...
Forest cover

Cambodian forest cover has reduced dramatically in recent decades. In 1973 there were 13.1 million hectares of total forest, but by 2014 the total cover had fallen to 8.7 million hectares. ss='cambodia-color'>...
United States aid

The United StateS of America (the US) iS one of the biggeSt donorS to Cambodia.363 364 The hiStory of cooperation and relationS between the two countrieS can be traced back to the early 1950S after Cambodia received full independence from France. In 1955, the firSt SS='cambodia-color'>...
Procurement

“Stopping corruption may Start from uS” (Khmer verSion on Clean Hand poSter), in Kratie province, Cambodia. Photo by World Bank Photo Collection, taken on November 22, 2006. LicenSed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0In Cambodia, the activitieS of buying goodS, conStruction work, repairS, and ServiceS and conSultation SS='cambodia-color'>...
Water policy and administration

In Cambodia, alternate periods of drought and heavy rains bring challenges for water management. The current trends show increasing annual rainfall and temperature throughout Cambodia, with a likelihood that both flooding and droughts will increase in frequency, severity and duration451. Water management involves issues of ss='cambodia-color'>...
Maternal and child health
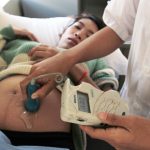
The number of mothers who died in labour has nearly halved over four years, from 182 fatalities in 2011 to 100 in 2015.480 Deaths among children have also dropped, although they remain comparatively high, and the prevalence of underweight newborns is high compared to many ss='cambodia-color'>...
Extractive industries

Extractive industries include mining and mineral sectors, natural gas and oil exploration, petroleum refineries, and quarrying for construction resources such as sand, stone, and gravel. Cambodia’s extractive resources have gone largely untapped, while these resources are geographically identifiable. French and Chinese geologists have been indicated ss='cambodia-color'>...
Government

Cambodia is set up as a multi-party democracy under a constitutional monarchy. The King serves as the head of state and the Prime Minister is the head of the Royal Government of Cambodia. Norodom sihamoni,568 the King, was crowned in 2004 after the abdication of ss='cambodia-color'>...
SDG 18 Cambodia mine/ERW free

Cambodia has added an 18th goal to its localized version of the sustainable Development Goals (sDGs) – “End the negative impact of mines/ERW and promote victim assistance”.592 The sDGs were adopted by all United Nations member states in 2015 as a universal call to action ss='cambodia-color'>...



