Maternal and child health
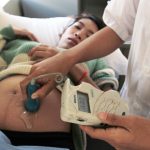
<p>The number of mothers who died in labour has nearly halved over four years, from 182 fatalities in 2011 to 100 in 2015.1 Deaths among children have also dropped, although they remain comparatively high, and the prevalence of underweight newborns is high compared to many ...p>
Copper

<p>Copper exploration is concentrated in preah Vihear province in the northern part of Cambodia. The most active explorer is Australian-based Geopacific Resources, in collaboration with Cambodian tycoon Kith Meng’s Royal Group. Geopacific Resources is working with Cambodian-based Royal Group at Kou Sa, a 158 km2 ...p>
Coal

<p>Although exploratory work has indicated the presence of modest coal resources in northern Cambodia, no commercial-scale mining has yet begun. The coal used in electricity generation and for other purposes is imported.A coal barge from Samarinda coal mine on the Mahakam river. Indonesia, Borneo. photo ...p>
Small and medium enterprises SME

<p>Small and medium enterprises (SME) have long been considered a vital driver to economic growth for developing economies. SMEs stimulate job creation throughout the country. Migration of employment to neighboring countries and the unemployment rate has significantly decreased due to a rising number of SMEs, ...p>
Agricultural policy and administration

<p>Agriculture in Cambodia accounts for approximately 56% of the labour force. The size of the sector means that policies developed here have a significant impact on the whole country. Agricultural policy and administration is managed by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF). There ...p>
Environmental and biodiversity protection

<p>Cambodia is one of the most biodiverse countries in Southeast Asia. Biodiversity supports Cambodians ecologically, economically and culturally. It plays an important role in providing ecosystem services and economic development to achieve the Cambodian Millennium Development Goals including poverty reduction. ...p>
On-shore oil and gas exploration and extraction

<p>Nineteen onshore blocks have been delineated for possible oil exploration. Contracts have been awarded for three. No oil is currently extracted in Cambodia. ...p>
Renewable energy production

<p>Renewable sources of energy include biofuels, solar, wind, tidal and geothermal energy. Fossil fuels such as petroleum or coal are not renewable. ...p>
Forest policy and administration

<p>Logging truck in Mondulkiri protected forest , Cambodia. photo by Global Water Forum, taken on 23 February 2014. Licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0Cambodia is deeply concerned about deforestation. While the country seeks fast economic development, forests represent a tremendous national treasure. In order to help ...p>
Marine and coastal areas

<p>In terms of attractiveness, one of Cambodia’s assets is the relative absence of intense development along its coasts, in comparison with neighboring countries. The 440 kilometer-long coastline includes a large area of non-urbanized zones, where locals can make their livelihoods from coastal resources. Cambodia’s coastline ...p>
Solid waste

<p>Trash collection in Siem Reap province, Cambodia. photo taken by David Villa, taken on 12 January 2008. Licensed under CC BY 4.0 DEED.Solid waste is defined as “used things, materials, or products that remain or are generated from human daily activities and livelihood and do ...p>
Concessions

<p>A land concession is a grant of rights over an area of land for a specific purpose. In Cambodia land concessions can be granted for various purposes, including agribusiness, redistribution of land to the landless and land-poor, infrastructure development, mining and fishing. They have been ...p>
Protected areas

<p>As Cambodia emerged from years of conflict, pressures grew on natural resources and sensitive areas. In response, a number of protected areas were created by royal decree in 1993 to protect ecologically and culturally important places. More detailed guidelines on managing the country’s protected areas ...p>
Off-shore oil and gas exploration and extraction

<p>For the purposes of oil and gas exploration, six Offshore Blocks (A–F) have been set out. Significant finds of oil have been made in Block A, but no oil has yet been extracted. ...p>
Agricultural production

<p>Rice field in Cambodia’s countryside. photo by fmpgoh, taken on 15 July 2009. Licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0The main products from the agriculture sector are rice, rubber, corn, vegetables, cashews and cassava. Unprocessed agricultural exports were projected to be more than 90 percent of total agricultural ...p>
Chinese aid

<p>Construction of a laboratory funded by Chinese money. photo by Michael Coghlan, taken on 10 January 2014. Licensed under CC-BY-SA 2.0China, while once being at odds with the current government, is now Cambodia’s largest development partner. The two nations have grown increasingly close in recent ...p>
Forests and forestry

<p>Cambodia’s forests have seen a significant reduction of total forest and dense forest cover in recent years, the growth of plantations, particularly rubber, and an ongoing problem with illegal logging. ...p>
Forest classifications

<p>The classification of forests is set out in the Law on Forestry 2002. The law applies to both natural forests and plantations, and “defines the framework for management, harvesting, use, development and conservation of the forests in the Kingdom of Cambodia. The objective of this ...p>





